PETER
Phonesthemes Encoder from Transformer Embedding Representation
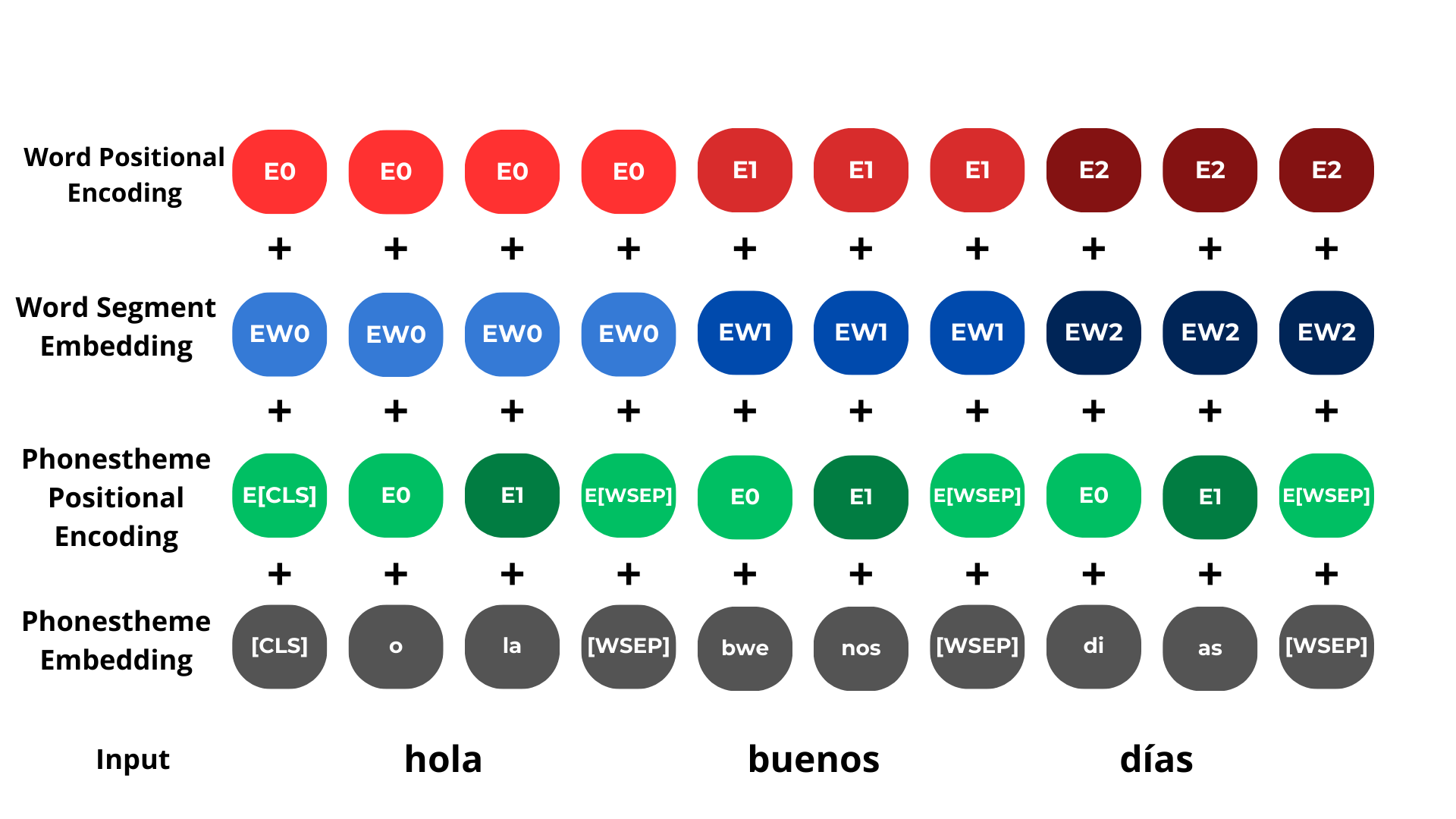
PETER is a novel transformer-based architecture designed to process and understand phonesthemes (sound-meaning patterns) in text using a multi-layered embedding approach. It combines phonestheme embeddings with positional encodings and word-level information to create rich text representations.
Architecture Overview
PETER uses four main types of embeddings that are combined:
- Word Positional Encoding: Tracks position of words in the sequence
- Word Segment Embedding: Vector representation of complete words
- Phonestheme Positional Encoding: Tracks position of phonesthemes within words
- Phonestheme Embedding: Vector representation of phonesthemes (sound units)
The model processes text by:
- Breaking words into phonesthemes using syllabification
- Converting text to IPA (International Phonetic Alphabet) representation
- Applying multiple embedding layers
- Processing through a transformer encoder
- Generating predictions at the phonestheme level
Installation
- Clone the repository:
git clone git@github.com:VerbaNexAI/PETER.git cd PETER - Create and activate a virtual environment (optional but recommended):
python -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate # On Windows use: venv\Scripts\activate - Install required packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Project Structure
.
├── data/ # Training and testing data
├── experiments/ # Jupyter notebooks for testing
├── logs/ # Training logs
├── models/ # Saved model weights and embeddings
├── src/ # Source code
│ ├── embeddings/ # Embedding implementations
│ ├── tokenizers/ # Text tokenization modules
│ └── utils/ # Helper functions
Usage
Basic Example
from src.peter import TransformerEncoder
from src.tokenizers.phonestheme_tokenizer import PhonesthemeTokenizer
from src.tokenizers.word_tokenizer import WordSegmentEmbedding
# Initialize tokenizers
phonestheme_tokenizer = PhonesthemeTokenizer(
model="models/phonestheme_embedding_es.model",
max_length=150
)
word_tokenizer = WordSegmentEmbedding(
model="models/word_embedding_es.model",
max_length=512
)
# Initialize model
model = TransformerEncoder(
phonestheme_tokenizer=phonestheme_tokenizer,
word_tokenizer=word_tokenizer,
vocab_size=8000,
d_model=150,
nhead=5,
num_layers=6
)
# Load pretrained weights
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("models/peter_model_trained.pth"))
# Process text
text = "hola buenos días"
phonestheme_tokens = phonestheme_tokenizer.encode(text)
word_tokens = word_tokenizer.encode(text)
output = model(
input_ids=phonestheme_tokens["input_ids"].unsqueeze(0),
attention_mask=phonestheme_tokens["attention_mask"].unsqueeze(0),
word_input_ids=word_tokens.unsqueeze(0)
)
Training
The model can be trained using your own data. Check the notebooks in the experiments/ directory for training examples.
Requirements
Main dependencies:
- Python 3.8+
- PyTorch 2.0+
- epitran
- pylabeador
- gensim
- num2words
See requirements.txt for complete list.
License
This project is licensed under the terms of the LICENSE file included in the repository.
Citation
If you use this work, please cite:
@article{PETERpaper,
title={PETER: Phonesthemes Encoder from Transformer Embedding Representation},
author={E. Payares, E. Puertas, J.C. Martinez-Santos},
year={2024}
}
Contact
For questions or issues, please open an issue in the repository.